Flatfoot (Pes Planus)
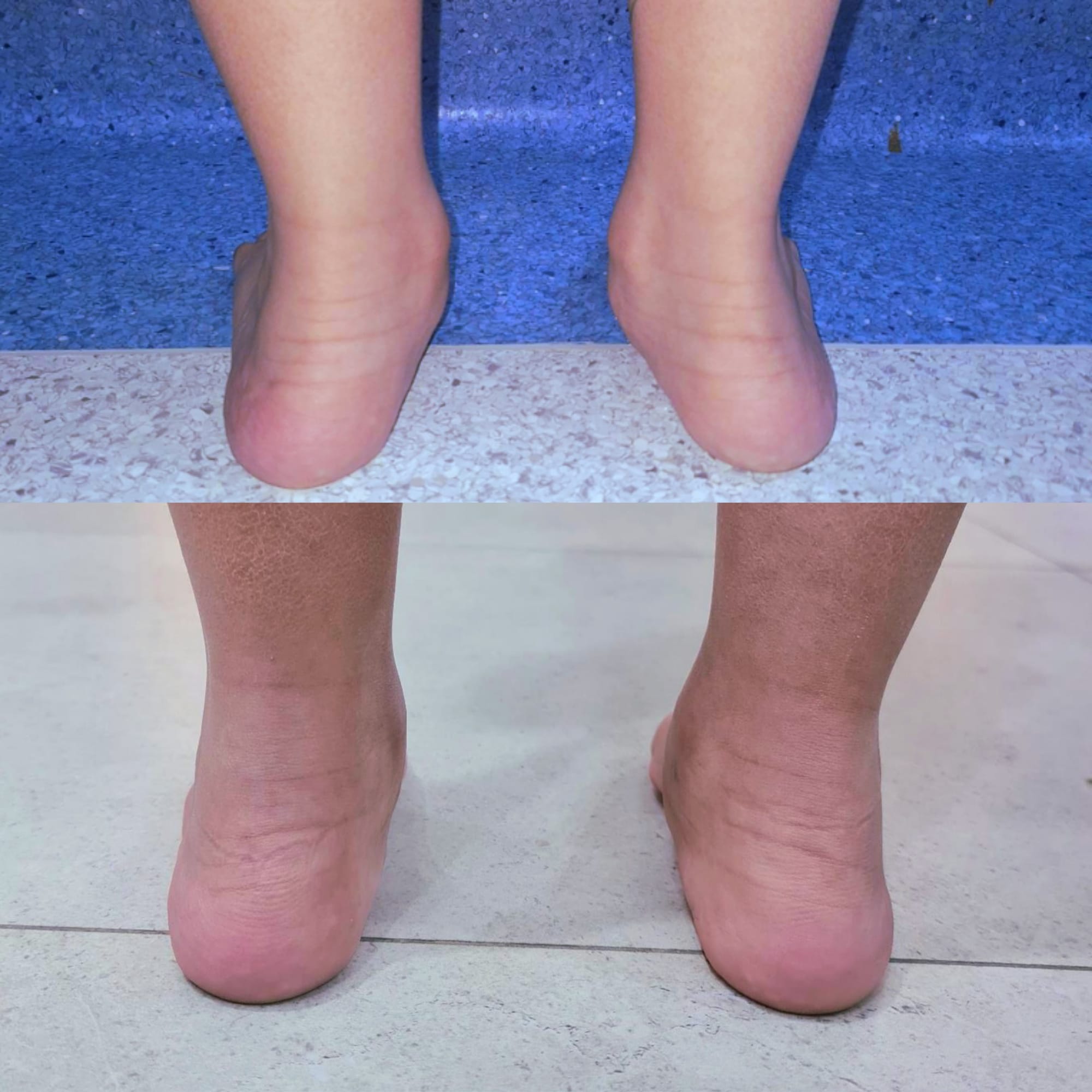
Flatfoot (Pes Planus) is a common condition frequently encountered in foot and ankle surgery clinics. In many cases where flatfoot is not associated with significant pain, conservative management is considered the optimal treatment option, including footwear modification and physiotherapy.
However, surgical intervention becomes the treatment of choice in certain situations, such as:
- Severe pain during walking or standing for short periods, significantly limiting the patient’s ability to perform daily activities.
- Severe flatfoot deformity in children and adolescents, where early intervention is required to prevent future progressive deformity.
- Painful congenital tarsal coalition between the hindfoot bones.
- A painful accessory navicular bone.
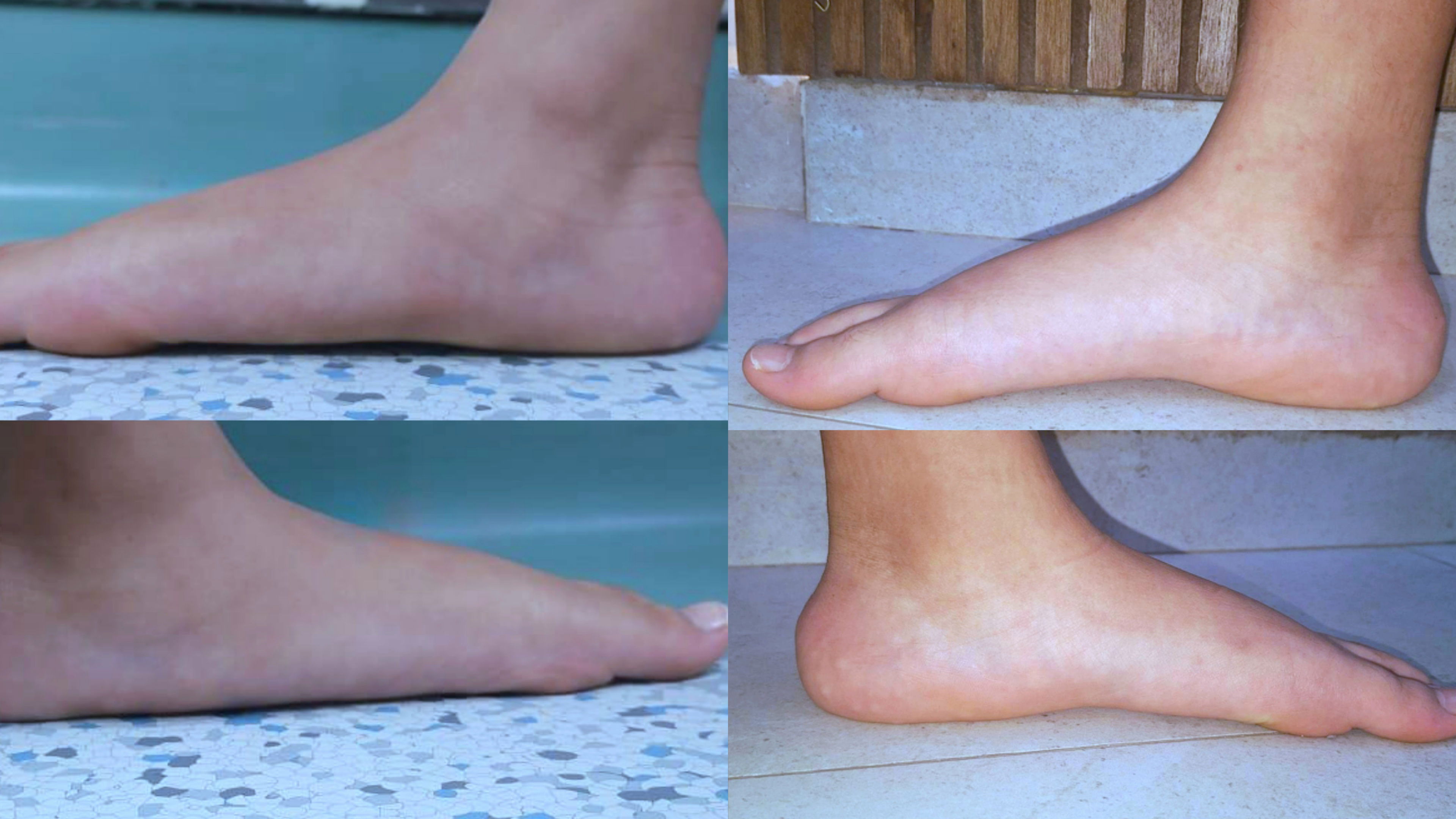
Classification of FlatfootAccording to age of onset:
- Congenital flatfoot: Appears at an early age and may be associated with generalized ligamentous laxity or congenital tarsal coalition.
- Acquired flatfoot: Occurs secondary to trauma or degeneration/rupture of the posterior tibial tendon or the medial ankle ligaments.
According to the condition of the subtalar joint:
- Flexible flatfoot: The subtalar joint remains mobile.
- Rigid flatfoot: The subtalar joint has restricted mobility, as seen in cases of congenital hindfoot coalition.
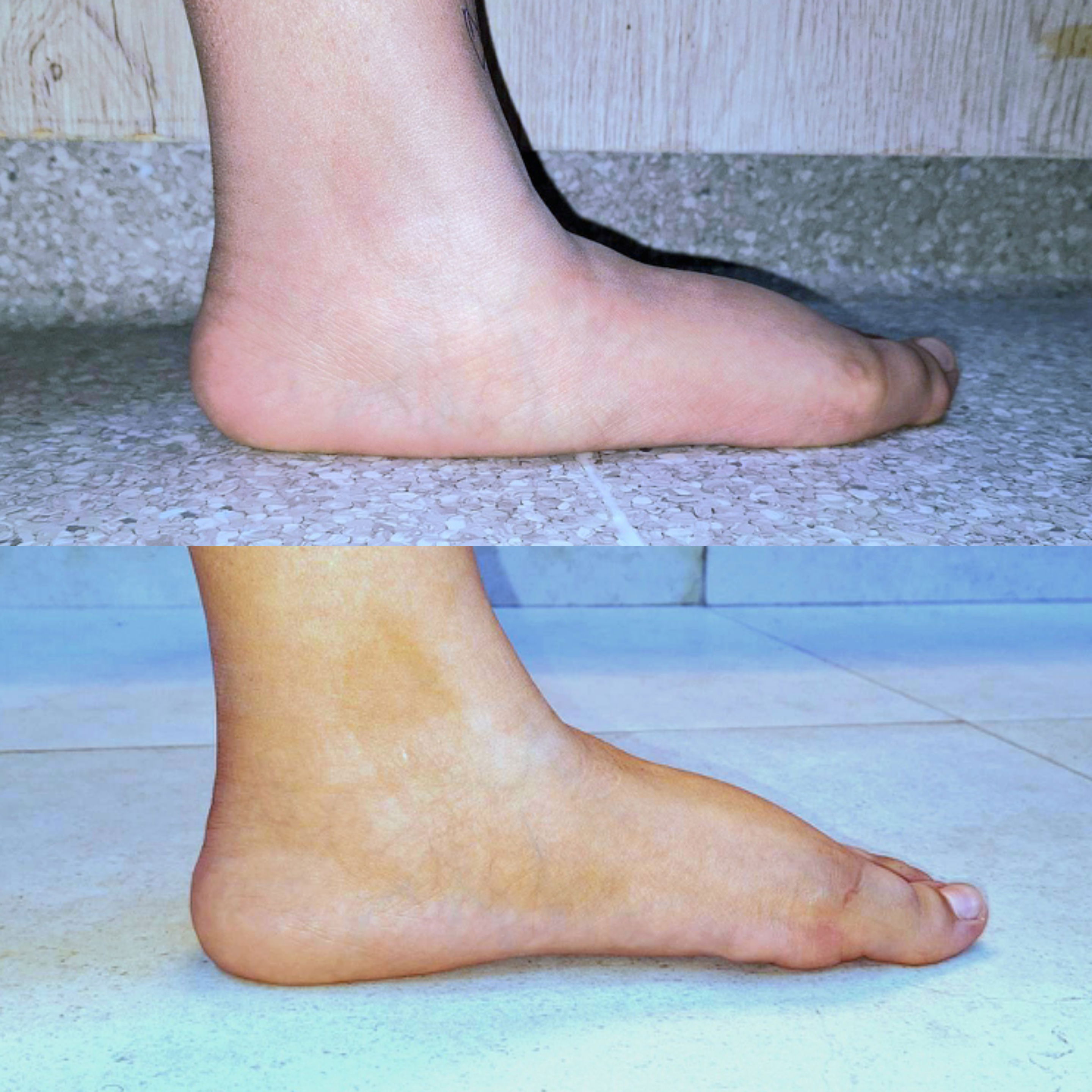
Evaluation and Management A thorough clinical examination and appropriate imaging studies are essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan, which may include:
- Subtalar arthroereisis (implant insertion): A procedure suitable for children aged 9–11 years, often combined with gastrocnemius muscle lengthening.
- Corrective osteotomy: An appropriate option for older patients without degenerative changes in the hindfoot joints.
- Hindfoot joint fusion and realignment: Indicated in cases of advanced degenerative arthritis of the hindfoot joints.
Outcomes The success rates of surgical procedures performed to correct flatfoot deformity are high and promising, with many patients experiencing significant improvement in function and quality of life following correction.
Example Text


